How to Show Users in MySQL and User Information Using Linux

A MySQL database server is frequently the first choice for developers and anyone interested in testing a structured query language. MySQL includes numerous features that make it dependable, secure, and efficient.
There are, however, some ways to improve MySQL server security even further. One of them is to create database users with restricted access.
This tutorial will explain why you should create separate MySQL user accounts and how to use the MySQL SHOW USERS command on your VPS.
Why Create Users in MySQL Server
Whenever users or database administrators install MySQL, the first user that will be created is the root user – the MySQL administrator. The root user will have permission to do everything on the MySQL database.
While having all the permissions can seem beneficial, doing so comes with its own security flaws, and sharing the root user between several people is dangerous. Hackers often try to log in as the root user and steal the hosted information or even destroy the whole MySQL server alongside its data.
Thus, system administrators create users with specific permissions on some databases. In other words, if credentials for one account get compromised, the impact will be minimal and manageable.
How to Show Users in MySQL Database on Linux
Unlike the SHOW DATABASES or SHOW TABLES commands that display all databases or tables right away, the SHOW USERS command does not exist in MySQL. Even though there is no such command, users can use a MySQL query and get a full list of users in a given MySQL database server.
Follow the steps below for more information.
1. Log in as the MySQL Root User
Start by logging in to the VPS via SSH as the root user. Once that’s done, enter the MySQL command line with this command:
sudo mysql -u root -p
Then, enter your MySQL root password.
Important! Keep in mind that system and MySQL root passwords are separate and can differ.
Once you are in the MySQL console as the root user, you will be able to run queries to display other MySQL users.
2. Use the MySQL SHOW USERS Query
Use the following query to show MySQL users created in the database server:
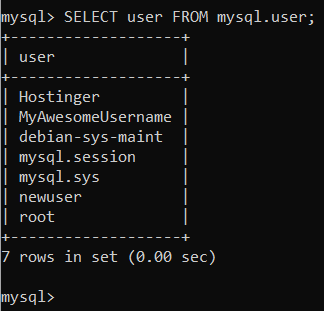
SELECT user FROM mysql.user;
As a result, you will see the list of all the users that have been created in MySQL.
Take note that there might be duplicate users. This is because MySQL filters access to a server according to the IP address it comes from.
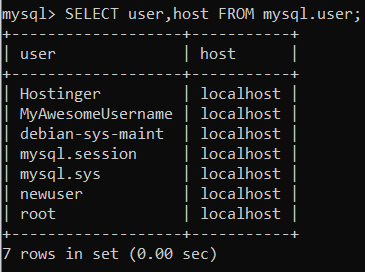
You can also add a host column to see even more information using the following command:
SELECT user,host FROM mysql.user;
With this, you will be able to see the MySQL users and which host or IP address they have permission to access. In our case, all of the users are from a local database:
3. See More MySQL User Information (Optional)
If you need more information about MySQL users, the search command can be expanded with the help of MySQL queries.
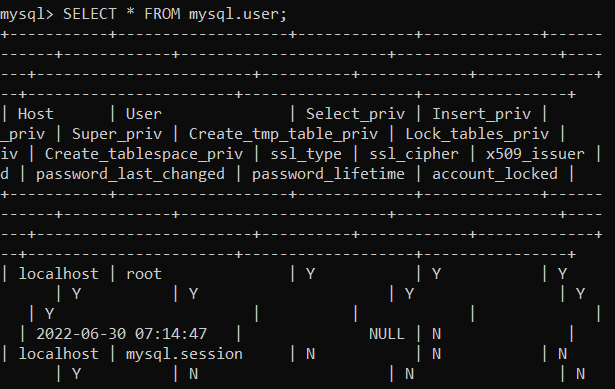
For example, the following command will print out all possible information from the user table:
SELECT * FROM mysql.user;
However, such output might look too messy to figure out. Thus, we recommend narrowing the search by using more specific queries.
Here are some of the more popular use-cases:
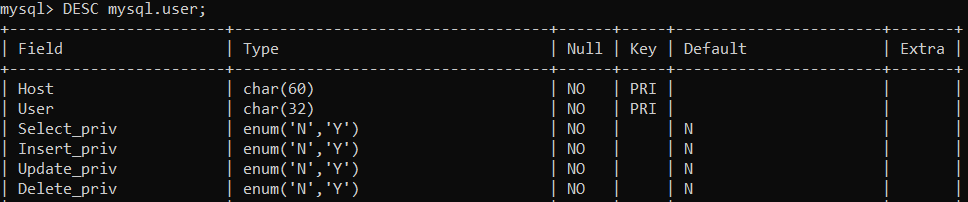
Preview Table Columns
The following query will display a preview of user table columns. It is especially helpful if users want to check information about a specific table.
DESC mysql.user
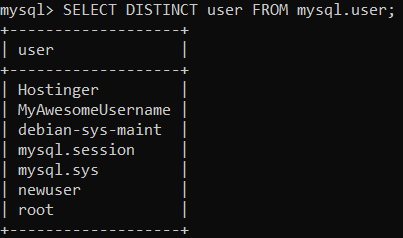
Display Only Unique Usernames
To skip repeating usernames, the following query can be used:
SELECT DISTINCT user FROM mysql.user;
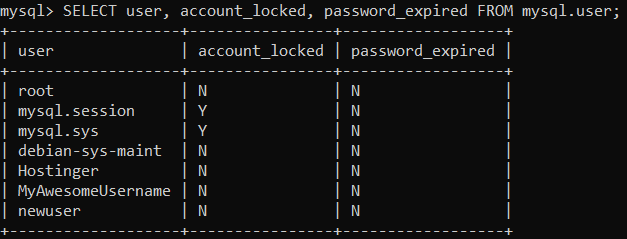
Password Expiration and Account Locking Status
In order to check the password expiration status and account locking state, use this query:
SELECT user, account_locked, password_expired FROM mysql.user;
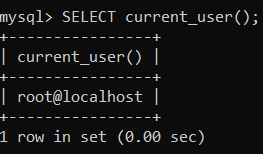
Show Current and Current Logged Users
The current user can be displayed with the following query:
SELECT current_user();
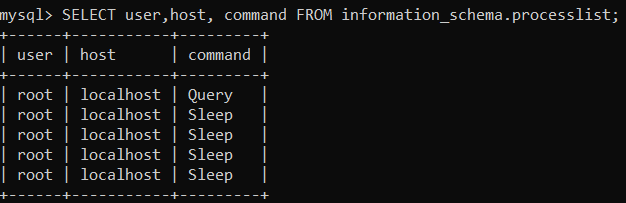
If you need more information, you can modify the query to display currently logged-in users with their states. This command is beneficial for finding idle users that use up too many resources.
SELECT user,host, command FROM information_schema.processlist;
Conclusion
The administration of a database server can be challenging work. Thus, database administrators must be careful when creating and administering user permissions.
The MySQL SHOW USERS command allows administrators to view MySQL users alongside other important information.
To recap, we’ve covered the basics of how to show MySQL users tied to a database and learned how to:
- List all users created in a given MySQL database
- Preview MySQL database table columns
- Display only the unique usernames in a table
- Check password expiration and account locking status
- Show current and currently logged-in users in a MySQL database
We hope that you found this tutorial helpful. If you have any additional questions or insights, let us know in the comments section below.
Learn More About Database Management Systems
What Is a DBMS: A Complete Guide
How to Install phpMyAdmin on CentOS 7
How to Install MongoDB on Ubuntu
Apache Cassandra: A Tutorial for Beginners
How to Install PostgreSQL on Ubuntu
How to Install phpMyAdmin on Ubuntu
How to Install PostgreSQL on CentOS 7
MySQL Show Users FAQ
How Can I See All MySQL Users and Passwords?
Make the following SQL query:
mysql> select user, password, host from mysql. user
This query brings up a list of users, their usernames, passwords, and database host.
How Do I Show Users in MySQL MariaDB?
Log into your MariaDB/MySQL server with the mysql client as a root user. Type the following query:
$ mysql -u root –p
Or
$ mysql –u root –h localhost –p mysql
Where Are Users Stored in MySQL?
MySQL stores users in the user table within the database.