Proxy vs VPN: What’s the Difference? Privacy, Security and Pricing Compared

Both proxies and Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) can conceal your IP address, giving your internet connection a layer of privacy. However, that’s generally the extent of the proxy vs VPN similarity.
There are significant differences between proxies and VPNs with regard to their pricing and the level of privacy and security offered. But the main difference between a proxy and VPN is that a proxy works only with a single service or app, while a VPN will encrypt all data and traffic.
This article will compare proxies and VPNs and explain the key differences between the two, helping you choose the best solution for your needs.

What’s the Difference Between Proxy and VPN?
The main difference between proxy and VPN is that a proxy server acts as an intermediary between the user and the internet, while a VPN encrypts all internet traffic and routes it through a remote server. While both can be used to enhance online privacy and security, a VPN offers stronger protection by encrypting all traffic, while a proxy only offers limited anonymity by hiding the user’s IP address.
Proxy vs VPN: Definitions and Key Differences
A proxy server acts as the middleman between a computer and a website or web-based application. It sends web requests on behalf of the computer and then returns the results.
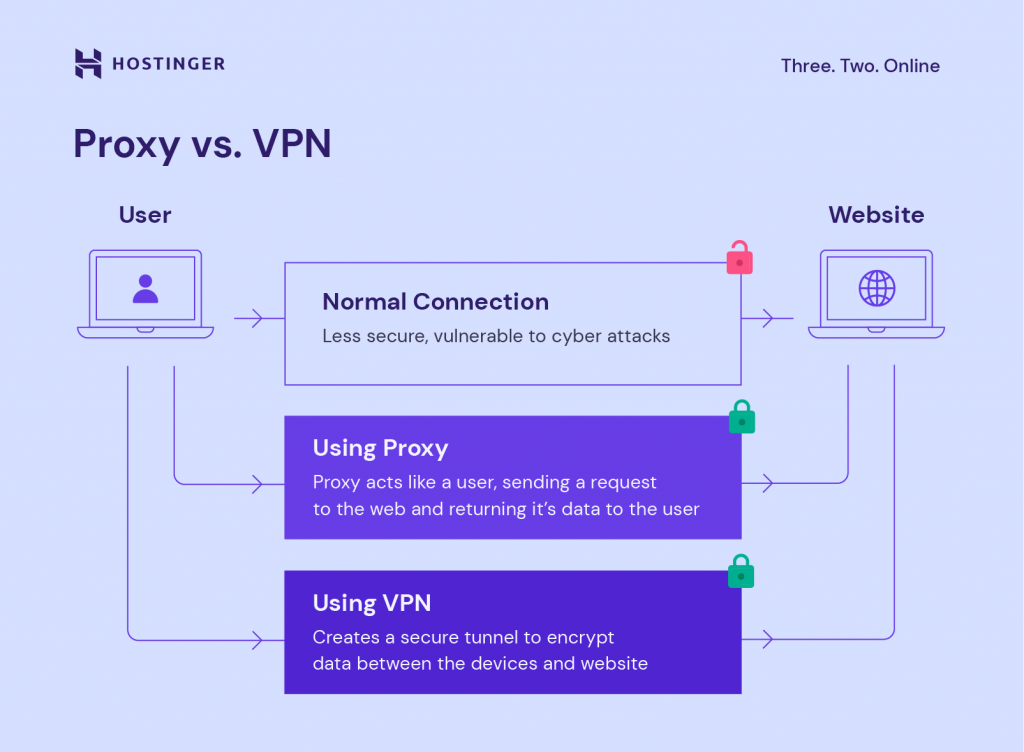
Because there’s an intermediary between the computer and the web, the user’s online activity is attached to a different IP address belonging to a remote host server. While connected to a proxy server, users’ real IP addresses are hidden.
Proxy servers may be located anywhere in the world. Users can choose the proxy server location they want, configure it in a specific web app, and connect to the internet under that location’s IP.
There are many types of proxies. The three most commonly used ones include:
- HTTP proxy. They’re used to view websites anonymously or access geo-restricted content.
- SOCKS proxy. These proxies are used for apps and other web-related purposes outside of the HTTP or HTTPS protocol, such as video streaming apps, P2P sharing, or games.
- Transparent proxy. Also known as inline proxies, they are used by network administrators to control online activity, such as blocking access to specific websites and web pages.
A Virtual Private Network (VPN) establishes a secure tunnel for an internet connection, masking a computer’s IP and encrypting the data exchanged between the device and the web.
To establish a VPN connection, a VPN client must be installed on a computer first. Once it’s activated, the web requests sent by the computer will be encrypted and routed by the client through the chosen website hosting server before finally reaching the target server.
Once a request is processed, information is sent back to the computer using the same data encryption process.
In a nutshell, a VPN service protects a user’s actual IP address and makes it extremely difficult for people to intercept their sensitive data.
Despite some similarities, there are some major differences between a proxy and a VPN:
- A VPN is configured at the operating system level, while a proxy is set up on an application-by-application basis. Once connected to a VPN, internet traffic from all apps and background processes will be routed through secure VPN servers.
- All VPNs encrypt data – many proxy servers don’t. Proxy servers are more prone to snooping and data theft by malicious third parties.
- VPNs are generally faster and more stable than proxy servers. Top VPN companies use quality servers and provide generous bandwidth to their users, while many public proxies are poorly maintained.
- VPNs are more user-friendly than proxies. A VPN is much easier to set up – all you have to do is download the VPN service’s app and connect to a VPN server of your choice. Setting up a proxy, on the other hand, involves entering the chosen proxy’s IP address and port number into an application’s network settings.
- VPNs are better for bypassing geo-restrictions and accessing region-locked content on streaming services like Netflix and Hulu. In general, most available proxies don’t have the sophisticated unblocking technology that some VPNs have.
- Quality website security software, including VPNs, tend to be costly, while the most commonly used proxy servers are free. A quality VPN service costs around $5-$10/month, while many HTTP proxies are publicly available for free.
Proxy vs VPN: Features Comparison
To learn more about the differences between proxies and VPNs, let’s compare their features in a more in-depth manner.
Web Browsing Performance
When it comes to fast and reliable connections, VPNs are faster and more stable than most proxy servers.
The top VPN services use modern servers with massive bandwidth that’s distributed to their users. They employ engineers who monitor and maintain servers to ensure they’re always in the best shape. As a consequence, users can stream videos and play online games with minimal latency.
However, connection interruptions do occasionally happen with VPNs because of server overload. Thankfully, switching to another server through the VPN’s app or client is very easy.
On the other hand, most proxies tend to be more unpredictable when it comes to connection speed.
Many free HTTP proxy server connections are slow and unstable – some can even go offline without notice. Fast proxy servers exist, but many of them offer a less secure connection. Some proxies are fast just because they are unencrypted, so be aware of this risk.
VPNs also come out on top when it comes to bypassing geo-restrictions on websites like Netflix or Hulu. With a VPN enabled, users can watch movies or TV shows that are not available in their current location.
Unfortunately, it’s way more challenging to find a proxy that can bypass sophisticated proxy blockers.
As an example, most proxies struggle to unblock foreign content in China because of The Great Firewall. Fortunately, a few top VPN companies have sufficient technology to bypass these restrictions.
All things considered, VPNs demonstrate better web browsing performance overall.
Privacy
When it comes to privacy, both a VPN and a proxy can mask a computer’s original IP address, allowing you to browse the internet anonymously.
But if you’re serious about your internet privacy, there are other important factors to consider.
A big concern for a lot of internet users is Internet Service Provider (ISP) tracking. Your ISP automatically logs your internet activity, whether you use your browser’s incognito mode or not. Here is what ISPs are known to keep track of:
- Browsing history
- Time spent on each website
- Type of device used
- Geolocation
- Online searches
- Emails
To keep your browsing activity hidden from your ISP, use a VPN. Some ISPs may be able to see that you’re connected to a VPN and are sending encrypted data to a remote server, but that’s the extent of it. Your browsing history and other potentially sensitive data remain hidden.
With a proxy, your ISP can see that you’re using a proxy and which proxy it is. Depending on whether the proxy uses encryption, your ISP may still be able to track your online activity. If avoiding ISP tracking is one of your goals, steer clear of unencrypted proxies.
However, ISPs and websites are not the only entities that can see your online activity. The owner of the remote servers you’re connected to – whether it’s a VPN or a proxy server – can see it too. This is why it’s essential to choose a trusted VPN or proxy service.
Fortunately, many of the top VPN providers have a strict no-logs policy. This means that they won’t keep track of any of your online activity.
If a government agency or another party requests your data, a VPN provider with a no-logs policy won’t be able to hand it over because it never kept any in the first place.
On the other hand, free proxy server operators can see all of your online activity. If you open non-HTTPS websites, any data you enter will be visible to them.
Many public proxy server operators are anonymous, so it’s difficult to be sure whether they’re monitoring your activity. Avoid using a public proxy server for data-sensitive activities and choose a trustworthy proxy service instead.
Pro Tip
If you want to add more layer of privacy, consider getting a domain privacy protection. It hides the WHOIS information associated with your domain from the public.
Security
A VPN service and a public proxy offer drastically different levels of security.
VPN connections are end-to-end encrypted. Top VPN providers deploy various military-grade encryption technologies, such as the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) with 256-bit keys that are virtually impossible to crack.
When using a VPN, the data that travels from the originating computer to the website and back is unreadable to third parties. This prevents possible attackers from stealing your sensitive information, especially when you’re connected to public networks like at a coffee shop or an airport.
On the other hand, not all proxies are encrypted. Most free HTTP proxies are unencrypted, so data travels in plain text form in and out of the remote computer server. With your data including usernames and passwords out in the open, you’ll be at risk of data breaches.
What’s even more concerning is the fact that 68.5% of free online proxies engage in suspicious activities, such as not allowing encrypted HTTPS, modifying JavaScript, or injecting ads. Therefore, free HTTP proxies must be completely avoided or used with extreme caution.
When it comes to security, VPNs also offer a broader scope of device protection. Unlike a proxy, a VPN is configured at the operating system level, which means that all of the computer’s web traffic – including background processes – will be routed through the VPN.
To ensure consistent protection, some VPN providers have a feature called the kill switch. When enabled, it will automatically turn off internet connection if the VPN routing stops for any reason. This prevents your actual IP address and data from being leaked by accident.
In contrast, a proxy must be manually set up at the application level. If you only configured a proxy on a browser, outbound internet traffic from other applications will remain under your real IP address.
In conclusion, the top VPN services are more secure than the majority of free proxy servers. However, you should also take other website security measures to avoid getting your website hacked, or ULR blacklisted.
Pricing
Both VPNs and proxy servers have free and paid services to choose from, contributing to your website maintenance cost.
When general consumers refer to using a proxy, they often mean utilizing a free proxy service like Hidester or manually setting up a public proxy from websites like Free Proxy List.
If your only concern is hiding your IP and you don’t care about data security, free proxy servers are good enough as long as you don’t use them to handle sensitive information.
Meanwhile, many premium proxies are geared toward businesses that conduct data collection, market research, and digital marketing. As a consequence, they tend to be quite expensive. For example, Smartproxy’s most affordable residential plan costs $75/month.
On the other hand, both free and premium VPN services are very popular among consumers.
On average, quality VPN services cost around $5-10/month. With the level of protection and the number of features you get, paying for a VPN is well worth the money. Most VPN companies offer a 30-day money-back guarantee as well, so you can claim a refund if you’re not satisfied.
However, we advise against using free VPN services, which usually come in an app or a browser extension. Unfortunately, many of them have been proven to conduct tracking and contain malware, defeating the purpose of using a VPN in the first place.
If you insist on trying a free VPN, look for trustworthy VPN companies that offer free trials, such as Windscribe, ProtonVPN, and Hotspot Shield.
Which One Should You Use, Proxy or VPN
Generally, VPNs are all-around better than most proxy options. However, the best choice for each user will depend on their needs.
If you’re only looking to mask your IP address or bypass geo-blocking without exchanging sensitive information, a proxy server will be enough.
If you’re looking for an all-inclusive solution to hide your IP, protect sensitive information, and bypass even the most sophisticated geo-blocking like the Great Firewall of China, a VPN is easily the better choice.
Can I Use Both Proxy and VPN?
Technically yes, but it’s not recommended. Connecting to a proxy server and a VPN adds an extra step in your web connection process and may significantly slow down your internet connection.
To keep your online activity private and maintain a stable connection speed, using a VPN that masks your IP address and encrypts your web traffic will be more than enough.

Conclusion
Both proxy servers and VPNs can effectively mask your original IP address, but they have stark differences in other aspects.
When it comes to performance, VPNs are faster and more stable than proxies. Some VPNs also allow their users to bypass and unlock some of the most sophisticated geo-restrictions. In contrast, widely available proxies tend to be very slow and rarely good at unblocking content.
VPNs are also better for online security. They establish an encrypted tunnel for all web traffic, preventing third parties from snooping or stealing your data. Most proxies, however, don’t encrypt your data, leaving it visible to attackers.
Overall, premium VPN services are better for protecting your activities and identity online. A quality VPN service will cost you around $5-10/month.
We hope this article has helped you decide between a proxy and a VPN. If you have any questions, feel free to leave them in the comment section below.

